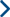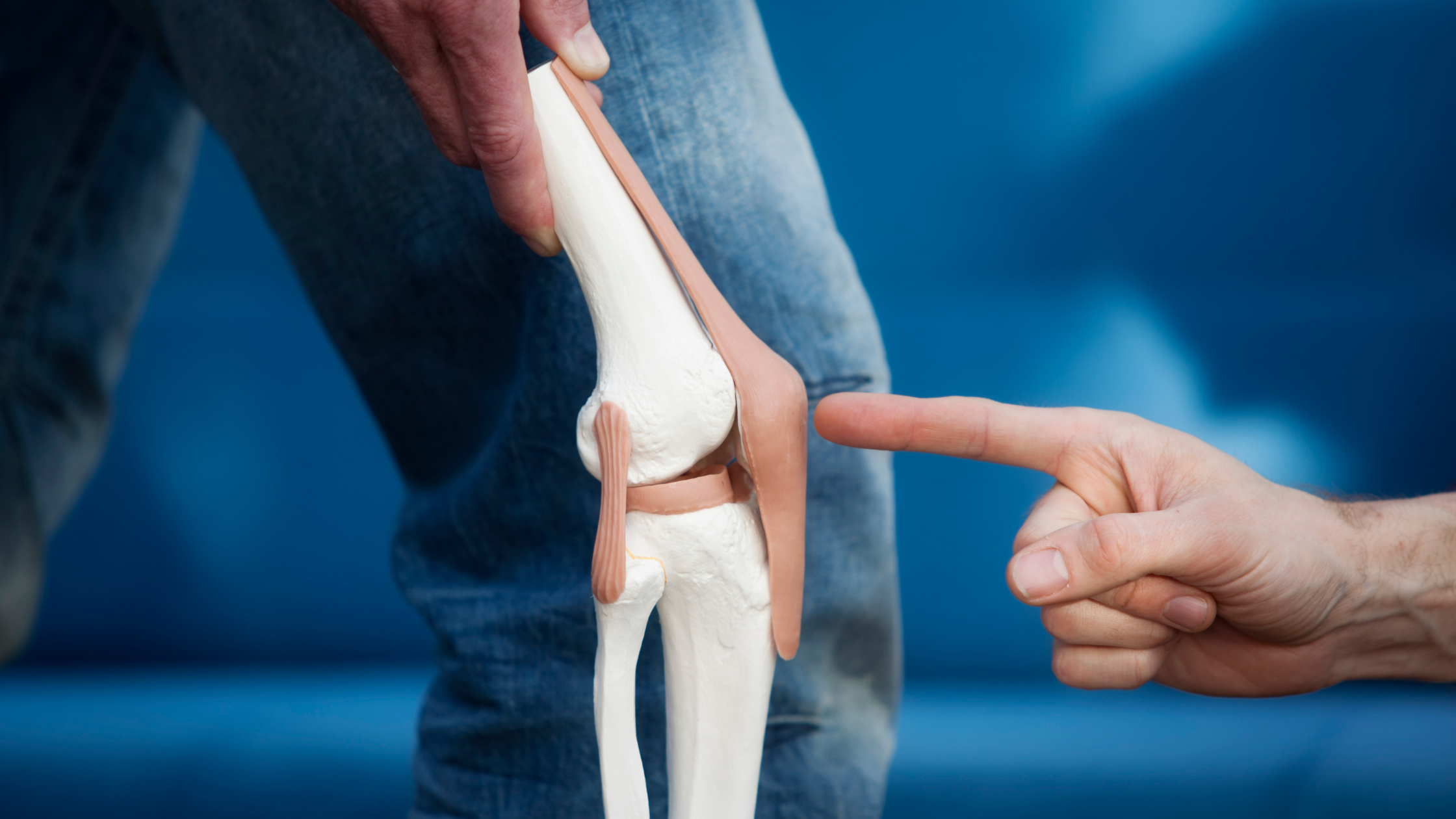
Are You a Candidate for Joint Replacement?
Joint pain is a common complaint, especially as people age or deal with chronic conditions such as arthritis. When conservative treatments like medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes fail to provide relief, joint replacement surgery can become a viable option. But not everyone with joint pain is a candidate for this procedure. So, how do you know if joint replacement is right for you?
This article will explore what joint replacement involves, the types of joints commonly replaced, who makes a good candidate, and the key factors that surgeons consider before recommending the procedure.
What Is Joint Replacement?
Joint replacement, also known as arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or worn-out joint is removed and replaced with an artificial one (prosthesis). The goal is to relieve pain, improve mobility, and enhance the quality of life.
The most common types of joint replacements include:
-
Knee replacement
-
Hip replacement
-
Shoulder replacement
-
Elbow and ankle replacements (less common)
These artificial joints are typically made from metal, plastic, or ceramic materials and are designed to mimic the function of a natural joint.
Signs You May Be a Candidate
Joint replacement is generally considered after non-surgical treatments have failed. Below are signs that may indicate you are a potential candidate:
1. Persistent Joint Pain
If you experience chronic joint pain that interferes with daily activities—even while resting or sleeping—this may signal advanced joint damage.
2. Limited Mobility
Stiffness and reduced range of motion in your joint, making it difficult to perform routine tasks like walking, climbing stairs, or getting out of a chair, are red flags.
3. Ineffective Non-Surgical Treatments
You’ve tried medications, physical therapy, injections, or other interventions for at least six months with minimal or no relief.
4. Joint Deformity
Visible deformities in your joint, such as a bowed leg or significant misalignment, often suggest severe structural damage.
5. X-Ray or MRI Evidence
Imaging that shows severe joint degeneration, loss of cartilage, or bone-on-bone contact is a strong indicator that surgery may be needed.
Common Conditions That Lead to Joint Replacement
Several underlying health conditions contribute to the need for joint replacement:
-
Osteoarthritis: The most common cause, characterized by the gradual wearing away of joint cartilage.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition that causes chronic inflammation and joint damage.
-
Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Develops after an injury to the joint, such as a fracture or ligament tear.
-
Avascular Necrosis: Occurs when the blood supply to a bone is disrupted, leading to bone tissue death.
-
Congenital Deformities or Dysplasia: Conditions that affect joint development can lead to early degeneration.
Who Is NOT a Good Candidate?
While joint replacement can be life-changing, it's not suitable for everyone. You may not be a good candidate if:
-
You have an active infection.
-
You have poor overall health or uncontrolled medical conditions (e.g., heart disease, diabetes).
-
You are significantly overweight or obese, which increases surgical risk.
-
You have unrealistic expectations about the surgery and recovery.
-
You are very young, and joint preservation techniques may be more appropriate.
These factors don't always rule out surgery but may require additional precautions or alternative treatments.
Evaluation Process: What Doctors Consider
Before recommending joint replacement, your orthopedic surgeon will conduct a comprehensive evaluation that includes:
1. Medical History
Your doctor will review your symptoms, how long you’ve experienced them, your pain levels, and previous treatments attempted.
2. Physical Examination
Range of motion, joint alignment, muscle strength, and your ability to perform basic movements will be assessed.
3. Imaging Tests
X-rays and MRIs help determine the severity of joint damage and whether the underlying condition is amenable to surgery.
4. Lifestyle Assessment
Your daily activity level, occupation, and personal goals will be factored into the decision.
5. Risk Assessment
Doctors also consider your age, weight, medical history, and other risk factors before recommending surgery.
Benefits of Joint Replacement
Joint replacement surgery has a high success rate, with most patients experiencing:
-
Significant pain relief
-
Improved mobility and function
-
Enhanced quality of life
-
Long-lasting results (modern prosthetics can last 15–20 years or more)
Risks and Considerations
As with any surgery, joint replacement comes with risks. Common concerns include:
-
Infection
-
Blood clots
-
Implant loosening or wear over time
-
Nerve injury
-
Need for revision surgery later in life
These risks are relatively low and can often be minimized with proper preoperative planning and post-surgical care.
The Recovery Journey
Recovery time varies depending on the joint replaced and the individual’s health. In general:
-
Hospital stay: 1–3 days
-
Initial recovery: 4–6 weeks
-
Full recovery: 3–6 months (sometimes up to a year for complex cases)
Physical therapy is crucial during recovery to rebuild strength, flexibility, and joint function.
Alternatives to Joint Replacement
If you’re not a candidate or want to postpone surgery, alternatives include:
-
Physical therapy and exercise
-
Anti-inflammatory medications
-
Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections
-
Assistive devices like canes or braces
-
Regenerative medicine (e.g., PRP or stem cell injections, still under study)
These options can provide temporary relief or help maintain function until surgery is necessary.
Conclusion
Joint replacement is not a first-line treatment, but it can offer dramatic relief and restore your ability to live an active life when other options have failed. If joint pain significantly affects your quality of life and conservative treatments haven’t helped, it's worth discussing surgical options with an orthopedic specialist.
Every case is unique. A thorough evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional will determine whether you are a suitable candidate. With the right approach, joint replacement can be a transformative solution for chronic joint problems.
Quick Links
Schedule an Appointment
* indicates a required field.