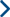
When to Consider Joint Replacement
Joint pain can significantly affect your ability to move comfortably, stay active, and enjoy daily life. While many people manage joint pain successfully with conservative treatments, there are times when joint replacement surgery becomes an important option to consider. Understanding when joint replacement may be appropriate can help patients make informed, confident decisions about their care.
Understanding Joint Replacement Surgery
Joint replacement surgery involves removing damaged portions of a joint and replacing them with artificial components designed to restore movement and reduce pain. The most commonly replaced joints include the knee and hip, though shoulder, ankle, and elbow replacements are also performed when necessary.
Joint replacement is typically considered after other treatment options have been explored and symptoms continue to interfere with quality of life.
Signs It May Be Time to Consider Joint Replacement
Joint replacement may be an option if you experience:
-
Chronic pain that doesn’t improve with medications, physical therapy, injections, or lifestyle changes
-
Pain that interferes with daily activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, sleeping, or standing from a seated position
-
Progressive stiffness or limited mobility that restricts movement and independence
-
Joint deformity, instability, or worsening alignment
-
Persistent pain at rest, including nighttime pain that disrupts sleep
When joint pain becomes constant and limits normal function, it may be time to discuss surgical options with a specialist.
Conditions That Often Lead to Joint Replacement
Several joint conditions may eventually require replacement, including:
-
Osteoarthritis, the most common reason for joint replacement
-
Rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory joint diseases
-
Post-traumatic arthritis following injury or fracture
-
Avascular necrosis, where reduced blood flow damages bone tissue
-
Severe joint degeneration unresponsive to non-surgical care
Each patient’s situation is unique, and the decision depends on symptoms, imaging findings, and overall health.
Trying Conservative Treatments First
Before recommending joint replacement, physicians typically explore non-surgical options such as:
-
Physical therapy and guided exercise programs
-
Anti-inflammatory medications or pain-relieving medications
-
Corticosteroid or viscosupplement injections
-
Weight management and activity modification
-
Bracing or assistive devices
-
Regenerative medicine or interventional pain management techniques
For many patients, these approaches provide meaningful relief and delay or eliminate the need for surgery.
Benefits and Considerations of Joint Replacement
Joint replacement can offer:
-
Significant pain reduction
-
Improved mobility and joint function
-
Better sleep and daily comfort
-
Enhanced quality of life
However, surgery also involves recovery time, physical rehabilitation, and potential risks. A thorough discussion with your healthcare provider can help determine whether the benefits outweigh the risks based on your individual goals and health status.
Is Joint Replacement Right for You?
Joint replacement is not based on age alone—it’s based on how much joint pain affects your life. If conservative treatments are no longer effective and pain limits your ability to function, a surgical consultation may be appropriate.
Working with a multidisciplinary pain or orthopedic care team can help ensure all treatment options are considered before moving forward with surgery.
Final Thoughts
Joint replacement can be a life-changing solution for patients with advanced joint damage and persistent pain. Understanding when to consider this option—and exploring all available treatments—empowers patients to make informed decisions about their long-term joint health.
If joint pain is holding you back, speaking with a specialist can help clarify your options and guide you toward the most appropriate next step.
Quick Links
Schedule an Appointment
* indicates a required field.